
1Department of Commerce, PSG College of Arts & Science, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Creative Commons Non Commercial CC BY-NC: This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 License (http://www.creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits non-Commercial use, reproduction and distribution of the work without further permission provided the original work is attributed.
Examining an industry’s technological upgradation is unexpected and unavoidable. The subsequent technical innovation is driven by the expectations and wants of the consumer for each product. History shows that switching from one technology revolution to another usually takes longer than the current trend. The industrial sector is currently faced with several risks, and it will take some time for management and staff to become used to new technology. This article presents the characteristics of both Industrial 4.O and Industrial 5.O and sustainability by using secondary data from various sources like journals, website, etc. The world has framed Sustainable Development Goals to know their pathway toward the sustainability of all living organisms and monitor their activities which will boost the countries to travel on a sustainable path and this article provides the keynotes about the goals. This article concludes that innovation in any domain should consider sustainability as the main theme.
Sustainability, economic growth, industry evolution, upgradation of technology
Introduction
An industry’s evaluation will pave the road for the growth of the economy. The fifth Industrial Revolution is now underway in developed nations. Mass transmission of goods and services and the use of artificial intelligence in most industrial processes are key goals. As every customer has a unique preference, the industry is moving more toward mass customization of goods and services. For every product consumer serves as the impetus for innovation and the technological revolution, as it paves the way to national progress along with sustainable development. Even economically prosperous nations will struggle to adopt manufacturing and educate their workforce in new technologies, so growing nations should analyse the factors that might act as barriers to adopting the new technology revolution. India is in the initial stage of 4.O technological adoption, whereas industrialized countries are in the initiation process of 5.O. India is exporting to developed countries like the UK, the US, and EU-27 even by lagging in technological advancement while comparing their local manufacturing domain. The main advancement in the 5.O is mass customization which is more in demand in foreign countries. India is in the practice of customization in the product but not in the mass volume of production. To compete in the global market, it is crucial to comprehend the technological advancements and industry revolution in the relevant sector. The higher levels of the industry are not feasible without any improvements and Industrial Revolution. Setting up new objectives and innovations on the worldwide market can draw customers and keep them loyal to innovative goods. The factors that cause the Industrial Revolution are new inventions, access to raw materials and rectifying the errors that occurred in the current era, trade routes, partners, social changes, a stable government, desire to get new things, customers need, etc.
Need for the Study and Structure
In the Industrial Revolution, industrialized nations are in the pre-phase of Industry 5.O, whereas the non-industrialized nations are in the Industry 4.O phase. The nations’ technological differences make the exporters face intense rivalry. Due to intense rivalry in the modern period, the companies are struggling in both the local and export markets. Analysing the factors, exporters find it difficult to upgrade the technology and solve the current problems. The following research questions (RQ) are attempted to be addressed by this study, which gives an overview of the problems with technological upgrades and sustainability measures.
RQ1. What are the elements that exporters face difficulty in competing in the global market as a result of technological advancement?
RQ2. What is the initiative taken for sustainability?
This article provides the answers to the RQ in two sections. The first section discusses the factors that make it difficult for exporters to compete in the global market as a result of technological improvement. The second discusses the government’s sustainability plan to ensure the continued expansion of the sector.
Research Methodology
Precise literature research was conducted to determine the overview of the industrial-technological revolution and the changes that were made in the process of producing goods and services. In Google Scholar, Research Gate, Scopus, and Web of Science, the phrases Industrial 4.O, Industrial 5.O, technological revolution, creation of new technology, and so forth were used to locate the pertinent articles. It should be emphasized that the research does not contain all the relevant articles; rather, it is limited to covering the most recent and significant advancements in the field and summarizing and giving readers an overview of the current situation and potential directions for the future. This article employs a descriptive research format.
Overview of the Technology Revolution
The entirety of the Industrial Revolution began in the early 1780s. The first revolution focused an emphasis on elements like railways, water and steam power, and automation. This forces the nations to produce the items at a rate that will satisfy half of the global demand. The second Industrial Revolution, which followed, began in the 1870s and brought advances like mass manufacturing, assembly lines, and the electrification of machinery to meet much of the demand. This was followed by the third Industrial Revolution, which began in the 1970s and brought about changes in machine automation, the use of computers in manufacturing, and the production of electronic devices in order to reduce labor requirements and better meet consumer demand. The fourth Industrial Revolution, which focuses more on the digitization of the entire process, the influence of the internet, and the introduction of artificial intelligence in the production process, is currently taking root in emerging nations. In the future, people will focus more on the fifth Industrial Revolution, which will emphasize mass-scale customization of manufacturing, the use of cobots in the production process, and the integration of cognitive systems across the whole process (Ahmad et al., 2020).
The time span for technological advancement is quite short when compared to the existing pattern of revolution. And because of the population and the need for distinctive items, there is more conflict than usual in the global market. Developing nations should keep pace with developed nations in terms of technology in order to capture a larger proportion of the global market (Figure 1). Developing nations should keep speed with developed nations in terms of technology in order to capture a larger proportion of the global market. The requirements of customers constantly shift which means they want to upgrade to the next level so they can take advantage of the opportunities (Duarte et al., 2018). Every Industrial Revolution has distinctive traits designed to meet the evolving demands of the global market. To make alterations and upgrades to the company’s current technology, it is crucial to identify that special trait. The customer, who rules the market, determines the direction of the Industrial Revolution. Now, consumers are more interested in customized products since it allows them to stand out from the crowd and attract attention. The nations with a sizable global market share began advancing toward the next stage of the Industrial Revolution in order to meet consumer demand. Whenever there is an Industrial Revolution, manufacturing companies struggle to adapt new technology in their workplaces and teach their staff how to operate them. In order to rectify them and to spice up the new implementation that offers benefits in all dimensions, it is of the utmost importance to assess the issues.
Figure 1. Time span for Technological Advancement.
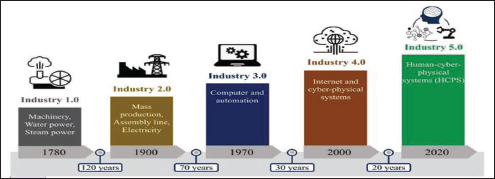
Source: Research Gate (2021).
Industry 4.O
Industry 3.O revolution processed out automation of manufacturing machinery, which further paved the way for Industry 4.O. This progression (Industry 4.O) focuses increasingly on the digitization of every step of the manufacturing process, which transforms how people connect, communicate, and do business. Literally, this revolution is causing an exponential and severe change in how people use technology, such as computers, to assist in their daily lives. Industry 4.O involves the development of 3D printing, intellectual property, artificial intelligence, smart robotics, and automation, as well as quantum computing, the Internet of Things, drones, the blockchain, and the utilization of big data (Faridi et al., 2020). The two main pillars of Industry 4.O are DIGITALIZATION and AUTOMATION IN MANUFACTURING (Happonen & Ghoreishi, 2021). Investors and international leaders became interested in this fourth Industrial Revolution due to its major keyways (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Major Break through in Industrial Revolution Pathway.
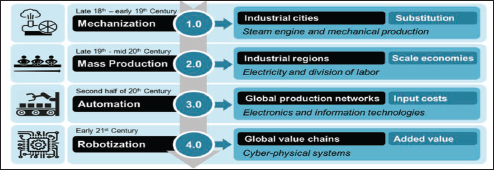
Source: Research Gate (2020).
Challenges in Adopting 4.O.
Lack of technology abilities is the main obstacle to adoption 4.O. To compete in the worldwide market, it is common to embrace the global situation in accordance with technological advancement. In the modern period, the manufacturing sector depended entirely on labor for most of its tasks. When the manufacturing sector begins to automate its processes, both the industry and society must go through a complete transition (Bongomin et al., 2020). Exporters must employ emerging technologies effectively if they want to prosper both domestically and internationally (Küsters et al., 2017). If a nation hindered technological advancement, it would lose market share both domestically and abroad. Among the risk factors for exposure to automation, the low level of adoption of automation may be the most significant. The minor obstacles to adoption in 4.O include concern regarding data security and privacy, lack of funds to adopt early, lack of appropriate digital infrastructure, requirement of specialized skills, training the employees and employers, unavailability of technological raw material, Credit facilities for technological upgradation, changes in the human working pattern, survival of small scale industries, need and want of the consumer identification process, competing with earlier adaptors, value chain integration, high investment requirements, uncertainty about economic benefits, lack of IT infrastructure and lack of internet coverage.
Highlights of Industry 4.O.
The core notion of 4.O is that humans can acquire and analyse data and make better judgments with the help of cutting-edge sensors, embedded software, and robotics (Rathore, 2022). The outcomes of using digital technology include increased automation, preventative maintenance, self-optimization of process improvements, and most crucially, a new level of efficiency and customer responsiveness (Chen & Xing, 2015). The Industrial Revolution, therefore, concludes with the following highlights in section 4.O IoT, IoS, Machine learning, Digitalization, Automation, Smart Industry, Cyber-physical system, Cognitive computing, made for me (Customization), Virtualization, Decentralized decision, Real-time capabilities (Ghoreishi, 2020).
Technology 5.O
The introduction of intelligent goods and automated machinery with robotics support is the main technical development of the fourth Industrial Revolution. Since artificial intelligence is being used for generating technology more than human contact, there will be several drawbacks. This is the key justification for switching to the fifth Industrial Revolution right now. With human assistance, the next revolutions will be more interesting, like those in business. In practical settings, automated AI systems cannot control the human experience. Undoubtedly, AI systems will help people, but they should not replace humans. The top technology enablers of Industry 5.O, are technological blockchain, drones, exoskeletons, additive technology, 5G and beyond, and mixed reality. Every invention in technology 5.O will have 5G connec tivity and robotics plays a vital role in the upcoming days. The 5.O enables smart infrastructure along with clean energy and intelligent transportation.
Highlights of 5.O
Industry 5.O will focus on
Sustainability
As everyone considers the development of technology, sustainability should also be given the same weight without fail. Only an ecologically sound environment throughout the world makes it feasible for humanity to move further in the direction of sustainable progress (Rathore, 2023). Even though new technology sped up production and made work easier, industrialization also brought forth new issues. Everyone should consider the mantra that SOUND GROWTH IS SUSTAINABLE GROWTH. Some of the negative effects included soil contamination, water pollution, and air pollution, all of which significantly reduced life expectancy and quality of life. All industries, from production to consumption, see sustainable growth as a result of technological advancement. In order to compete in the market, development is impossible without technological advancement. Every business, whether it is new or already established, wants to remain competitive for a longer period. The world is in an era where items may be customized, and consumers are going toward this trend. The only way for industrials to survive in the global market is to adapt to the world and to client wants. The manufacturing process should be expanded as the product’s demand rises, and the product’s shelf life should be examined. The market’s demand and preferences for the product will last for a certain amount of time before shifting to the next one. In order to fill the market with a product that meets the current need, the maker should identify the market, seize the moment, and seize the opportunity. Technology development plays an important role in this transaction, from acquiring the raw materials to gathering user feedback. Due to the free movement of commodities inside the nation, the product cannot survive in the market for a longer period without technological advancement within the organization. The points to be considered whenever the revolution happens in the aspect of sustainability (Faridi et al., 2020).
Global Sustainable Measures (SDGs)
The new inventions are moving forward with the primary purpose of sustainability for the environment, even as the world established the Millennium Development Goals and Sustainable Development Goals for the welfare of the people, to reduce poverty, and to ensure the people’s lifestyle (Ahmad, 2020). Recent innovations like cheap energy storage, long-term storage, plastic recycling, LED light efficiency, and public electric transportation create pollution-free environments daily. Only the countries that balance both technological upgradation and sustainability of the environment at the same ratio will move in the positive direction of economic growth. The Rio+20 conference on sustainable development produced the global sustainable development report, which is structured so that it will be examined once every four years to track how well a nation is doing in terms of achieving its sustainability goals. An impartial team of scientists chosen by the UN Secretary-General initially prepared the preceding global sustainable development report. The present study, which has been largely compiled by a committee of independent scientists, will be made public by September 2023. According to the 2023 report, the world has halfway completed the 2030 agenda, and everyone should hurry up their efforts that were delayed by COVID-19. According to the 2030 SDGs’ intended agenda goal, countries should focus more on realizing their goals. The report conveys that 89% of the least developed countries, 93% of landlocked developing countries, and 94% of small island developing states had food inflation above 5%. SDG’s goals like economic growth, industry innovation, and infrastructure, sustainable cities, and communities, responsible consumption and production, climate action, life below water, and life on land are inviting new inventions of technology upgradation. Technology should upgrade along with sustainability for steady economic growth.
Conclusion and Future Directions
The market and industry should adopt the most recent technology in the early adoption stage itself because technology is developing quickly. The company could only survive in the market for a longer period if it did this. The government should evaluate the pros and downsides of the technology that a specific industry is adopting, set sustainable goals, and monitor the industry to ensure that it is adhering to those goals. Currently, primarily a few nations have witnessed Industrial Revolution development 4.O, as the few developed countries are transitioning to Industry 5.O, which is mass customization of the products, and the need for product modification is currently at its pinnacle. High-market nations ought to be aware of technical advancements occurring elsewhere, and such nations ought to produce products for their domestic markets to prevent losing market share because doing so would cause their economies to inflate. Every citizen of developing countries and underdeveloped countries should be aware of the SDGs to support their country in achieving its vision that would be effective for the nations.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
ORCID iD
Deepana P.  https://orcid.org/0009-0007-9053-0716
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-9053-0716
Ahmad, S., Miskon, S., Alabdan, R., & Tlili, I. (2020). Towards sustainable textile and apparel industry: Exploring the role of business intelligence systems in the era of Industry 4.0. Sustainability, 12(7), 2632.
Bongomin, O., Nganyi, E. O., Abswaidi, M. R., Hitiyise, E., & Tumusiime, G. (2020). Sustainable and dynamic competitiveness towards technological leadership of Industry 4.0: Implications for East African community. Journal of Engineering, 2020, 1–22.
Chen, Z., & Xing, M. (2015). Upgrading of textile manufacturing based on Industry 4.0. In 5th international conference on advanced design and manufacturing engineering (pp. 2143–2146). Atlantis Press. https://doi.org/10.2991/icadme-15.2015.400
Duarte, A. Y. S., Sanches, R. A., & Dedini, F. G. (2018). Assessment and technological forecasting in the textile industry: From first industrial revolution to the Industry 4.0. Strategic Design Research Journal, 11(3), 193.
Faridi, M. S., Ali, S., Duan, G., & Wang, G. (2020). Blockchain and IoT based textile manufacturing traceability system in Industry 4.0. In International conference on security, privacy and anonymity in computation, communication and storage (pp. 331–344). Springer International Publishing.
Ghoreishi, M., Happonen, A., & Pynnönen, M. (2020). Exploring Industry 4.0 technologies to enhance circularity in textile industry: Role of Internet of Things. In Twenty-first international working seminar on production economics (pp. 16). Springer Nature.
Ghoreishi, M., & Happonen, A. (2021). The case of fabric and textile industry: The emerging role of digitalization, Internet-of-Things and Industry 4.0 for circularity. In Proceedings of sixth international congress on information and communication technology: ICICT 2021, London, Volume 3 (pp. 189–200). Springer Singapore.
Happonen, A., & Ghoreishi, M. (2021). A mapping study of the current literature on digitalization and Industry 4.0 technologies utilization for sustainability and circular economy in textile industries. In Proceedings of sixth international congress on information and communication technology: ICICT 2021, London, Volume 4 (pp. 697–711). Springer Singapore.
Küsters, D., Praß, N., & Gloy, Y. S. (2017). Textile learning factory 4.0—Preparing Germany’s textile industry for the digital future. Procedia Manufacturing, 9, 214–221.
Rathore, B. (2022). Textile Industry 4.0 transformation for sustainable development: Prediction in manufacturing & proposed hybrid sustainable practices. Eduzone: International Peer Reviewed/Refereed Multidisciplinary Journal, 11(1), 223–241.
Rathore, B. (2023). Textile Industry 4.0: A review of sustainability in manufacturing. UGC Approved Research Journals in India| UGC Newly Added Journals|(IJNMS), 10(1), 38–43.